|
|
|
BS Biomedical Engineering |
Biomedical engineering is an interdisciplinary area in which engineering expertise and design concepts are applied to problem solving in the life sciences and medicine. This Program focuses on understanding complex living systems and use of technology and advance systems to improve diagnosis and treatment.
Biomedical Engineering Program prepares students for productive careers and diverse profession including medical devices, pharmaceuticals biotechnology as professional education, and research. Biomedical Engineers have developed a number of life-enhancing and life-saving technologies including diagnostics, Therapeutic equipment, life supporting devices, surgical devices and systems, vital sign monitoring devices and prosthetics.
Biomedical Engineers works with a broad range of profession, ranging from other engineering specialties to basic laboratory scientist, to physician and nurses, and have strong communication skills that makes biomedical engineer the general interpreter for such a widely educated individual; the one who knows the language of both engineering and medicine.
|
THE SCOPE & JOB PROSPECTS |
Biomedical Engineering is one of the emerging fields which combines Engineering expertise with the needs in the medical industry for the growth and development of the healthcare sector. It is the unique branch of Engineering in which the concepts, knowledge, expertise and skills are designated and applied to the field of biology and medicine in order to meet the daily challenges. The field of biomedical engineering, as the term implies, includes the mathematical modelling of the biological systems, design and computation of the algorithms which help to analyze biological signals, bioinformatics, biomechanics, applications of micro-electromechanical systems, molecular engineering, nanotechnology and development of signal processing and control algorithms of artificial parts of the body.
- A biomedical engineer carries out various functions within the biomedical engineering industry and other institutions such as hospitals, healthcare organizations and teaching institutions.
- They design the sleek computer systems which help to monitor patients during the different stages of the hospital care. Moreover, they also build the systems to monitor the health aspects of the healthy persons.
- They design and build the complex sensors to measure blood chemistry, such as sodium and pH.
- They design the instruments and devices for the therapeutic uses for example the device for the eye surgery.
- They design clinical laboratories and automate different units within the hospitals and other health care delivery systems using the advanced engineering technologies.
- They design, build and investigate the medical imaging systems based on X-rays (Computer Assisted Tomography), Magnetic Fields (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), Ultrasound or newer modalities.
- They develop and implement the mathematical models of physiological systems for example they design and construct biomaterials and find out the mechanical, transport and biocompatibility properties of implantable materials
- They investigate the Bio - Mechanics of injury and wound healing.
- They develop new horizons in sports engineering in order to restore complicate sports technique and to reduce workload of coaches in efficient way.
- Design systems and products, such as artificial internal organs, artificial devices that replace body parts, and machines for diagnosing medical problems
- Install, adjust, maintain, repair, or provide technical support for biomedical equipment.
- Evaluate the safety, efficiency, and effectiveness of biomedical equipment
- Train clinicians and other personnel on the proper use of equipment.
Work with life scientists, chemists, and medical scientists to research the engineering aspects of biological systems of humans and animals. |
PROGRAM EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES |
The three program educational objectives (PEOS), as given below, form the basis of the B.S Biomedical Engineering Program at Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology LUMHS. The PEOS were formulated in the consultation with the members of faculty and were adapted by the institute of biomedical engineering for the implementation of outcome-based education (OBE).
Within the period of the graduation, the students with BS in Biomedical engineering are expected to attain the following objectives:
PEO-1: Apply the knowledge of mathematics, science, engineering fundamentals and create enabling technologies for the improvement of human health and health sciences.
PEO-2: Enhance students’ intellectual and analytical abilities in taking initiative and/or developing innovative ideas for technological and professional growth in the field of Biomedical Engineering.
PEO-3: Work effectively as a team member or lead multidisciplinary teams while demonstrating the interpersonal and management skills, ethical, social, and environmental responsibilities. |
PROGRAM LEARNING OUTCOMES (PLO) |
- ENGINEERING KNOWLEDGE
An ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, engineering fundamentals and an engineering specialization to the solution of complex engineering problems.
- PROBLEM ANALYSIS
An ability to identify, formulate, research literature, and analyze complex engineering problems reaching substantiated conclusions using first principles of mathematics, natural sciences and engineering sciences.
- DESIGN / DEVELOPMENT OF SOLUTIONS
An ability to design solutions for complex engineering problems and design systems, components or processes that meet specified needs with appropriate consideration for public health and safety, cultural, societal, and environmental considerations.
- INVESTIGATION
>An ability to investigate complex engineering problems in a methodical way including literature survey, design and conduct of experiments, analysis and interpretation of experimental data, and synthesis of information to derive valid conclusions.
- MODERN TOOL USAGE
An ability to create, select and apply appropriate techniques, resources, and modern engineering and IT tools, including prediction and modelling, to complex engineering activities, with an understanding of the limitations.
- THE ENGINEER AND SOCIETY
An ability to apply reasoning informed by contextual knowledge to assess societal, health, safety, legal and cultural issues and the consequent responsibilities relevant to professional engineering practice and solution to complex engineering problems.
- ENVIRONMENT AND SUSTAINABILITY
An ability to understand the impact of professional engineering solutions in societal and environmental contexts and demonstrate knowledge of and need for sustainable development.
- ETHICS
Apply ethical principles and commit to professional ethics and responsibilities and norms of engineering practice.
- INDIVIDUAL AND TEAMWORK
An ability to work effectively, as an individual or in a team, on multifaceted and /or multidisciplinary settings.
- COMMUNICATION
An ability to communicate effectively, orally as well as in writing, on complex engineering activities with the engineering community and with society at large, such as being able to comprehend and write effective reports and design documentation, make effective presentations, and give and receive clear instructions.
- PROJECT MANAGEMENT
An ability to demonstrate management skills and apply engineering principles to one’s own work, as a member and/or leader in a team, to manage projects in a multidisciplinary environment.
- LIFELONG LEARNING
An ability to recognize importance of and pursue lifelong learning in the broader context of innovation and technological developments.
|
OBE IMPLEMENTATION MODEL |
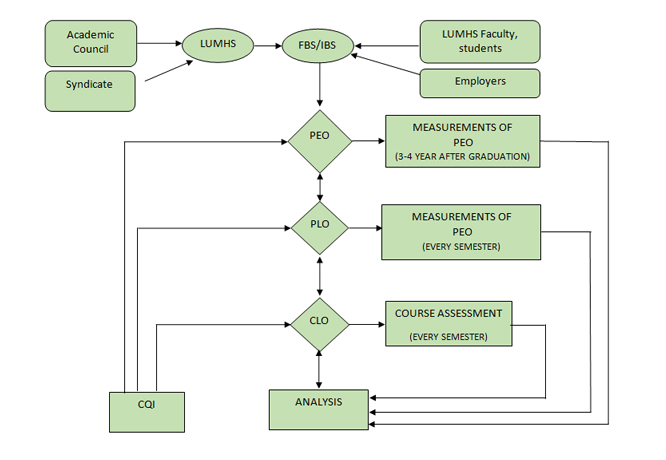
The overall process of assessment and evaluations of PEOS and continuous quality improvement (CQI) is shown in figure: the complete CQI process is based on the three concentric loops for assessment and evaluation. The PLOS (program learning outcomes) and CLOS (course learning outcomes) that ate described previously.
Various stakeholders are shown in the flow chart that are participate in the decision making process. The decision making process is explained in the following paragraphs.
LUMHS has a syndicate and an academic council. Institute has faculty board of studies (FBS) and institute board of studies (IBS) to handle various aspects of academic matters. The feedback is also provided by the institute faculty and students as well as by the alumni.
 |
| Download Prospectus 2024-25 |
|